Oracle Critical Patch Update Release
Oracle released their quarterly critical patch update today. This patch addresses a record number of 334 vulnerabilities across a wide set of Oracle supported products.
Vulnerabilities in Weblogic, Oracle Spatial, and Oracle Fusion Middleware MapViewer are rated with CVSS scores of 9.8. Deserialization based attacks within Weblogic server has been used as attack vectors in the past year, and used to install crypto miner campaigns. It is likely that these types of campaigns will continue for the forseeable future.
We recommend the review of the full CPU release to identify impacted software packages within your organization, and make plans to address those that create the largest risk. The full bulletin is available at Oracle at the URL http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/security-advisory/cpujul2018-4258247.html .
Scott Fendley ISC Handler
Searching for Geographically Improbable Login Attempts
For the human brain, an IP address is not the best IOC because, like phone numbers, we are bad to remember them. That’s why DNS was created. But, in many log management applications, there are features to enrich collected data. One of the possible enrichment for IP addresses is the geolocalization. Based on databases, it is possible to locate an IP address based on the country and/or the city. This information is available in our DShield IP reputation database. But you can also find coordinates with a latitude and a longitude:
$ geoiplookup isc.sans.edu GeoIP Country Edition: US, United States GeoIP City Edition, Rev 1: US, MD, Maryland, Bethesda, 20814, 39.006001, -77.102501, 511, 301 GeoIP ASNum Edition: AS62669 SANS INSTITUTE
The command geoiplookup, as well as the GeoIP databases, are developed by Maxmind [1] which is one of the companies which provide this kind of services. Of course, you can also create your own/private database of IP address (or subnets) and attach coordinates to them[2]. This is very useful if you operate a worldwide network or if you’re based in a large country like the United States. In this case, if subnets are assigned per branch offices, you can search for their coordinates via Google maps and populate your database:
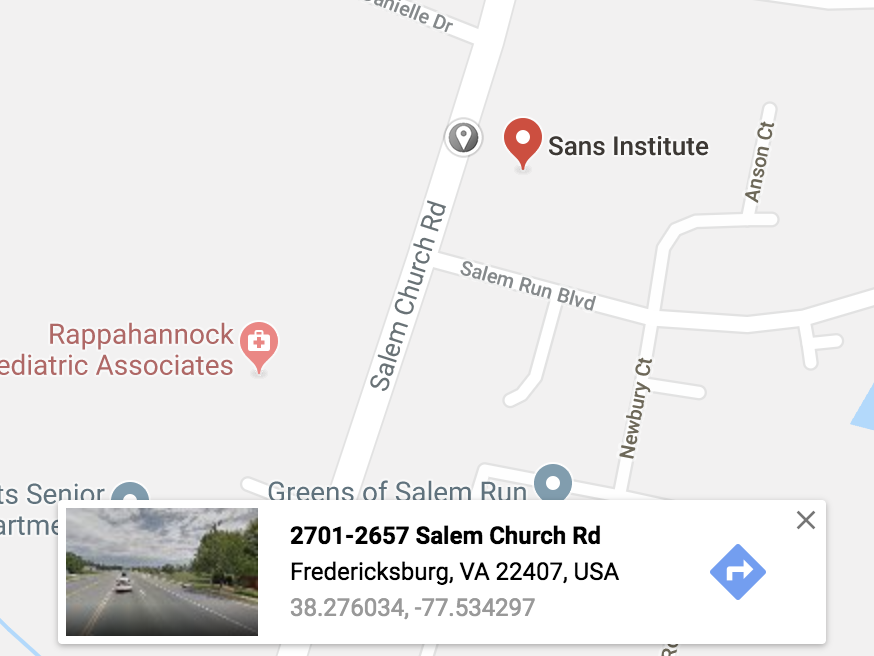
Once this exercise completed, the idea is to compute the distance between two IP addresses using the”Haversine” formula[3] which determines the distance between two points on a sphere given their longitudes and latitudes. Here is a quick and dirty Python script which implements the formula for two IP addresses GeoIP lookups:
#!/usr/bin/python
import sys
import geoip2.database
import math
def haversine((lat1, long1), (lat2, long2)):
radius = 6371 # In kilometers
dLat = math.radians(lat2 - lat1)
dLong = math.radians(long2 - long1)
a = (math.sin(dLat / 2) ** 2 + math.cos(math.radians(lat1)) * math.cos(math.radians(lat2)) * math.sin(dLong / 2) ** 2)
c = 2 * math.atan2(math.sqrt(a), math.sqrt(1 - a))
d = radius * c
return d
reader=geoip2.database.Reader('GeoLite2-City.mmdb')
r1 = reader.city(sys.argv[1])
r2 = reader.city(sys.argv[2])
print "%s: %s, %s" % (sys.argv[1], r1.country.name, r1.city.name)
print "%s: %s, %s" % (sys.argv[2], r2.country.name, r2.city.name)
d = haversine((float(r1.location.latitude), float(r1.location.longitude)), (float(r2.location.latitude), float(r2.location.longitude)))
print "Distance: %f Kms" % d
Let’s try:
$ host -t a isc.sans.org isc.sans.org has address 204.51.94.153 $ host -t a www.nsa.gov www.nsa.gov is an alias for www.nsa.gov.edgekey.net. www.nsa.gov.edgekey.net is an alias for e6655.dscna.akamaiedge.net. e6655.dscna.akamaiedge.net has address 23.206.125.32 $ python distance.py 204.51.94.153 23.206.125.32 204.51.94.153: United States, Bethesda 23.206.125.32: United States, Cambridge Distance: 629.667952 Kms
Now, we can implement more tests to detect unusual behaviours when consecutive connections are detected for the same username. Let’s assume that Johannes connected to my server at a specific time from isc.sans.org and, 15 minutes later, the same username was used from www.nsa.gov (this is just an example ;-). From a purely geographical point of view, this is suspicious and must be investigated.
The next checks can be implemented to detect geographically improbable login attempts:
- If the distance between the two connection attempts is <1000 Kms: we can assume that the user will take a train or a car to travel (a slow means of transport). The minimum time between two connections must be above 8 hours (let’s assume the speed up to 100Km/h).
- If the distance is above, we may expect that the user will use a plane to travel: 2 hours for the check-in process, a typical airliner is flying at ~800Km/h and add 2h to get out of the airport and travel to the final destination. We may assume a delay of min 24h.
It's up to you to analyze the behaviour of your users to apply efficient checks. This technique is quite easy to implement in your log management/SIEM solution (just a few math operations). By example, there is a Haversine app[4] available for Splunk.
Note: values have been computed using the metric system but for miles, divide km by 1.609344.
[1] https://www.maxmind.com/en/geoip2-databases
[2] https://github.com/threatstream/mhn/wiki/Customizing-Maxmind-IP-Geo-DB-for-Internal-Networks
[3] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Haversine_formula
[4] https://splunkbase.splunk.com/app/936/#/details
Xavier Mertens (@xme)
ISC Handler - Freelance Security Consultant
PGP Key

Comments